Most brain injuries affect the cerebral hemispheres. Each cerebral hemisphere (left and right) is divided into four sections (called lobes). Each lobe is responsible for different things but they are all connected and work very closely together.
How the brain works
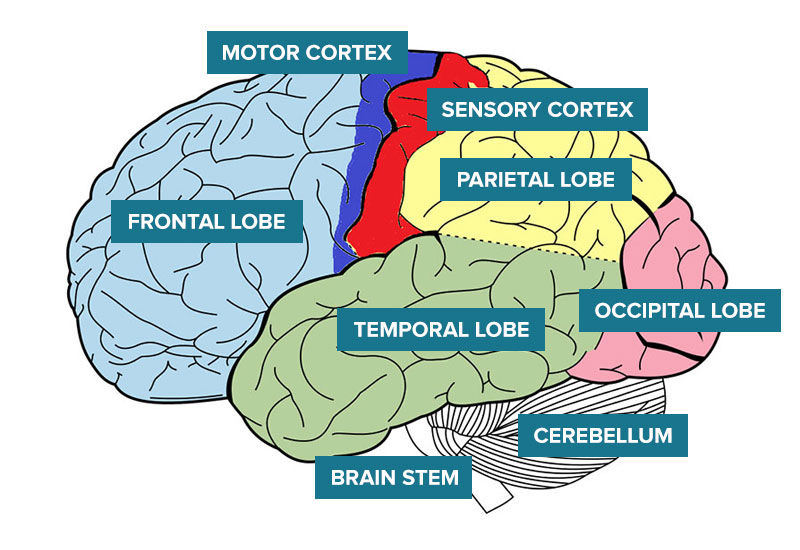
The left side of the brain controls movement and sensation on the right side of the body. The right side of the brain controls movement and sensation on the left side of the body.